Top Airline Pricing Strategies for 2025
Airline pricing is not guesswork.
It’s a structured approach based on market demand, competitor activity and customer behavior.
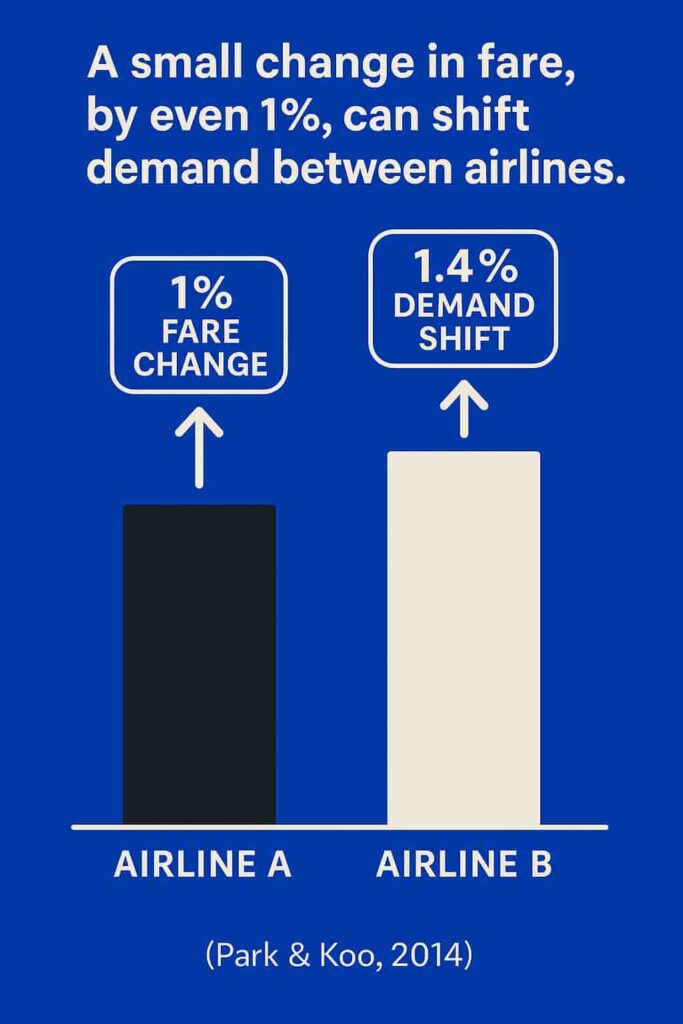
A small change in fare, by even 1%, can shift demand between airlines. In fact, Park & Koo (2014) found that when one airline raises prices, demand for another can grow by up to 1.4%.
For airline businesses, understanding how pricing works is key to staying competitive and profitable. Whether you’re managing routes, setting fares or reviewing market trends, pricing strategies play a central role in decision-making.
In this blog, we’ll explain the main types of airline pricing strategies and the factors that influence them. So you can better understand what drives price changes and how to respond.
How Do Airlines Set Prices?
Airlines set prices based on a mix of market demand, competition, operational costs, and dynamic pricing systems.
- Market Demand: Higher demand means higher ticket prices. Airlines adjust fares depending on how many people want to fly a certain route. If a flight is popular, prices go up. If demand is low, prices drop to attract more passengers.
- Competition: Airlines monitor what their competitors charge. If a rival airline offers a cheaper fare on the same route, they may lower their prices to stay competitive.
- Operational Costs: Fuel, labor, and maintenance impact ticket prices. If these costs rise, airlines often pass that increase onto passengers through higher fares.
Types of Airline Pricing Strategy
As per the unique airline business models, airlines adopt varying pricing strategies that help them generate hefty revenue.
Thus, we have listed the 4 most common types of pricing strategies that airlines generally use to enhance their revenue management.
All these include –
1. Legacy Pricing
Legacy pricing in airlines refers to traditional airline pricing strategies that have been in place for many years. These methods are typically used by established carriers to manage fares and maximize revenue. Unlike more dynamic pricing approaches, legacy pricing often relies on fixed rules and historical data. For instance, ticket prices may be set based on class of service, time of booking, and even the route’s popularity.
While effective in the past, legacy pricing can sometimes lack flexibility in today’s competitive market. This rigidity may prevent airlines from adapting quickly to changes in demand or competition.
2. Competitor-Based Pricing Strategy
Competitor-based pricing involves adjusting your prices in response to how rival airlines price similar routes. This approach is common because pricing in the airline industry is tightly linked across carriers.
According to research published by Evan Douglas from Griffith University, airlines watch each other’s fares daily, even hourly. If one carrier lowers its price, others often follow quickly to avoid losing bookings. This kind of reactive pricing helps protect market share, especially on competitive routes.
To manage this, most airlines use revenue management systems with tools like automatic fare matching and competitive tracking. These systems help airlines stay in sync with market movements and adjust fares without delay.
Demand is also highly price-sensitive. On most routes, especially where multiple airlines operate, even a small price drop can shift customers away from one airline to another. That’s why using a flight price API helps airline businesses stay updated on fare changes across the market and respond fast.
This strategy becomes even more critical in non-hub routes where no airline holds a dominant position. In these cases, pricing is more flexible, and customers tend to compare fares before booking. Smaller or low-cost carriers can use this to their advantage by slightly undercutting prices to attract more bookings.
For those looking to integrate live fare monitoring into their pricing strategy, FlightAPI offers access to flight price data through its API.
Here’s a quick tutorial to help you get started:
You can also explore their free trial to start testing real-time data today.
3. Penetration Pricing
It’s a method that is used by newcomers in the industry to gain a significant market share quickly.
Airlines that are recently introduced in the industry usually adopt a penetrating low fare to entice customers to fly on their flights and quickly make their place in the market.
4. Lowest Pricing Strategy
The lowest pricing strategy is another type of pricing tactic adopted by airlines to keep their fares lowest from the rest.
Usually, airlines that adopt this type of strategy focus on distinguishing themselves as the lowest-price provider in the market, in which they compete.
They adapt to the lowest cost of operations and ensure to keep their operating costs at the lowest to provide cheaper airfares.
A low-cost pricing strategy might not seem lucrative that generate massive revenue.
But, it is because these pricing strategies are designed to keep the flight fare lowest but charge a bit higher on other services like food, beverages, baggage, and more.
To get a deep insight into the lowest pricing strategy, check out the Ryanair (the most popular airline for the lowest prices) case study.
Ryanair’s approach helped it become Europe’s largest airline by passenger numbers in 2009. The airline cut its operating costs by 4%, hedged 90% of its fuel (saving £460 million), and grew its ancillary revenue from £3.6 million in 2007 to £5.9 million in 2009 through fees on extras like baggage and food.
You can explore the full case study to understand how Ryanair turned this model into a long-term advantage.
To apply this strategy effectively, you’ll need to track the lowest airfares offered by airlines across various OTAs. FightAPI can help you access this data in real time.
5. Value-Based Pricing
Value-based pricing strategy is the same as its name suggests and is based on travelers’ perceived value of a product or service.
Also, it keeps a check on the customer’s willingness to pay to determine their pricing.
One way of finding out how much your customers are willing to pay is by running surveys online and setting pricing accordingly, which includes your profit margin as well.
To know more about value-based pricing and how it is done in the airline industry, head over to this article.
6. Dynamic Pricing Strategy
If you would ask, what is the best pricing strategy for airlines and why?
Undoubtedly, dynamic pricing is considered to be the best pricing strategy for the airline industry.
Just as hotel rooms and holiday lets rates often vary during peak holiday seasons, airlines also experience similar variations in their pricing.
In short, dynamic pricing allows the airline industry to set its pricing based on real-time, demand, inventory, and other factors.
For creating dynamic pricing strategies, the airline industry uses different tools such as Flight Pricing API for pulling flight data and various data analytics tools to predict future demand and then adjust prices accordingly.
The benefits of dynamic pricing include:
(A) Maximize revenue
Dynamic airline prices are set using flight price forecasting data and historical data that allows airlines to charge more for seats in high-demand seasons and less for less popular seats, which maximizes revenue.
(B) Increase efficiency
Dynamic pricing also helps airlines to sell seats that they might lose due to unfair high pricing according to the current market trends. Which increases efficiency and reduces the risk of revenue loss.
(C) Improve customer satisfaction
Changing pricing according to seat types is also a part of the flight’s dynamic pricing strategy. By charging different prices based on different seat types. Airlines can offer a wider range of options to customers. Which can improve customer satisfaction and loyalty.
(D) Respond to market changes
Dynamic pricing allows airlines to quickly and easily respond to changes in market conditions, such as increased competition or unexpected events. Which helps them to make sure they are not over and undercharging.
(E) Data-driven decision-making
Dynamic pricing is based on data and analytics, which allows airlines to make pricing decisions that are based on solid data.
Now you’re aware of what benefits dynamic pricing strategy can bring to your airline business.
So, why not give it a try?
Although dynamic pricing is challenging to implement. But, you can leverage its benefits using the right technology to get accurate data such as FlightAPI to search flight prices, locations, flight names, dates & times.
As well as a good understanding of your market and customers.What Factors Affect Airline Pricing Decisions?
Factors That Accpet Airline Pricing
Airline Pricing Decisions vary greatly depending on numerous factors. And, here they are:
(A) Market demand
The level of demand for a flight or route can affect how an airline prices its tickets. If there is high demand for a flight, the airline may charge higher prices. Conversely, if there is low demand, the airline may lower prices to fill their seats.
(B) Competition
Changes in competitor’s pricing can have a greater effect on your airline’s ticket selling. To be competitive you can adjust your prices based on the prices of your competitors for the same flight or route.
(C) Cost of operations
Airlines need to consider the cost of operating the flight, including fuel, maintenance, and labor costs while setting ticket prices to make sure they are profitable.
(D) Route network
Pricing decisions may also depend on the route network of the airline. For example, prices for flights between major or popular cities may be higher than prices for flights between smaller cities. For getting flight route data, you can use FlightAPI.
(E) Seasonality
Airlines also adjust prices based on the time of year, as demand for flights may vary depending on the season.
For example, prices for flights during the peak summer travel season may be higher than prices for flights during the off-peak winter season.
(G) Distribution channels
Airlines may charge different prices for the same flight depending on where or how a customer books their ticket. For example, prices may be different for tickets booked directly through the airline’s website versus through a travel agent or online booking platform.
These factors are meant to keep on the top of mind while deciding pricing strategy for the airline industry.
If you still have a few questions regarding it, read the FAQs, and you might get the answer.
Frequently Asked Questions:
How Do Air Carriers Price Their Services?
Often airlines use a blend of different pricing strategies and take note of multiple factors before deciding their prices. It might include the cost of the aircraft, the total amount of fuel, operating costs of the airport, salaries of the workforce, and their profit margin.
In short, they decide the final flight pricing after removing the total operational costs plus their profit margin and dividing them by the average number of passengers to cover their costing.
Which Are The Most Used Airline Pricing Models And The Best One?
There are several pricing models used by airlines, including:
- Yield management: Similar to revenue management, but focuses on maximizing revenue per seat or per flight.
- Dynamic pricing: This model adjusts prices in real time based on demand and other factors.
- Fixed or Static pricing: This model sets prices based on a predetermined pricing structure, regardless of demand.
The best pricing model used in the airline industry is dynamic pricing which is based on current market demand and prices.
However, the best pricing model for an airline will depend on its specific business goals, route network, and competitive environment. Some airlines may find that a combination of different pricing models works best for them.
Final Words:
Airline pricing strategies are complex and involve a combination of different approaches to optimize revenue and stay competitive in the market.
These strategies allow airlines to adjust prices based on demand, market conditions, competition, route network, and other factors.
The key to successful airline pricing is understanding the market, and target customers, and being able to respond quickly to changes in market conditions.
Additionally, having the right technology, data, and analytics to make data-driven decisions is crucial.
The best pricing strategy for an airline will depend on its specific business goals, competitive environment, and route network. But, a combination of different pricing models can also work for them.